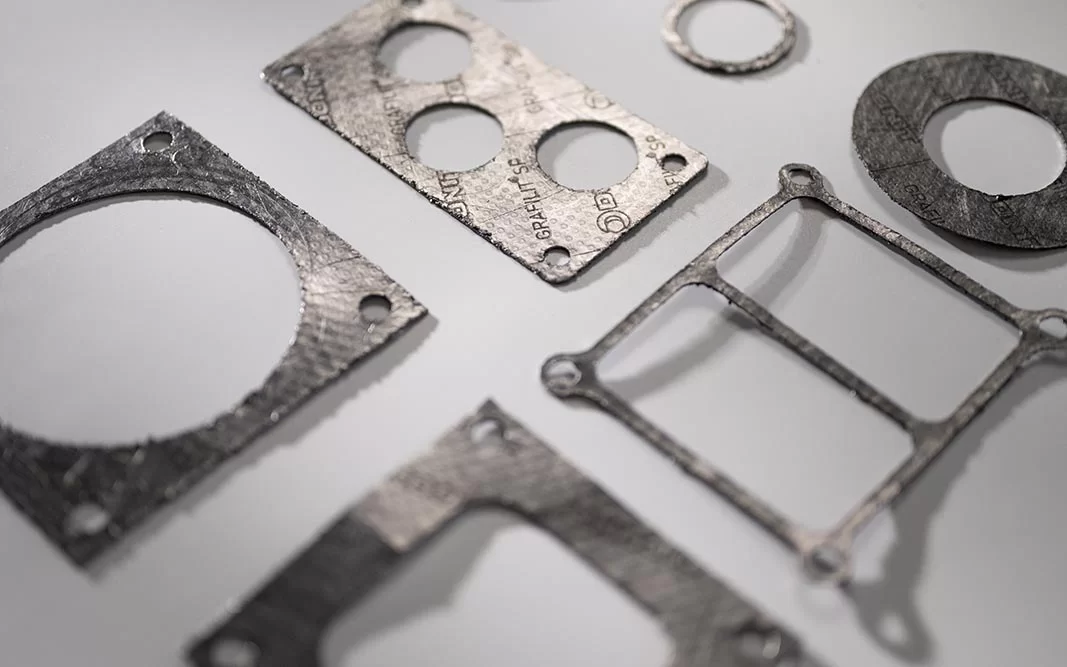
One of the many materials we use to manufacture gaskets is expanded graphite. Thanks to our CNC manufacturing technology, we can produce any shape cut or flat gasket from this material, both in small quantities and large series, precisely and efficiently.
Expanded graphite is a specialized material that, due to its exceptional combination of properties, finds application in many areas, especially for gasket manufacturing.
Expanded Graphite and Its Main Properties
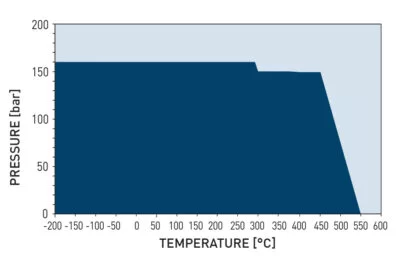
- Long-term temperature resistance -200°C to +550°C
- Maximum operating pressure 200 bar
- Excellent chemical resistance and stability
- Low permeability – gas permeability
- More about graphite, gasket manufacturing possibilities, and its applications can be found below.
Expanded Graphite
Graphite is available in several material variants, but the most commonly used type is expanded graphite reinforced with a stainless steel insert, which improves the material’s resistance and surface load and, especially in small thicknesses, reduces brittleness and improves handling.
Basic Material Properties for Gasket Manufacturing
| Composition | Expanded natural graphite (graphite content >99%) Stainless steel insert AISI 316 with a thickness of 0.1 mm |
| Color | Black |
| Certifications and Approvals | BAM (oxygen) | DNV GL | DVGW DIN 30653 (5 bar) | DVGW DIN 3536-6 | FIRE SAFE API607 |
| Standard Sheet Size | 1000 x 1000 mm | 1500 x 1500 mm |
| Available Thicknesses | 1.0 mm | 1.5 mm | 2.0 mm | 3.0 mm |
| Minimum Long-term Temperature | 200 °C / -238 °F |
| Maximum Long-term Temperature | 550 °C / 1022 °F |
| Maximum Operating Pressure | 200 bar |
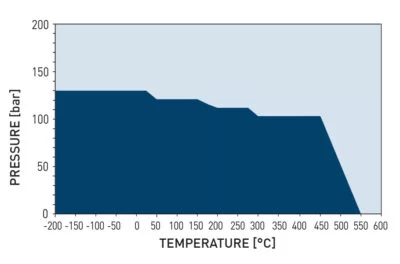
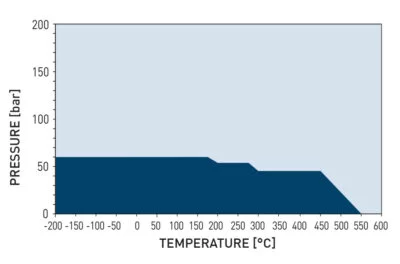
Operating Pressure Depending on Operating Temperature
Graphite Gaskets and Their Use in Industry
Graphite gaskets are key components in industrial applications where high demands are placed on sealing, thermal resistance, and chemical stability. Due to their unique properties, including high thermal resistance, chemical resistance, and the ability to adapt to irregular surfaces, graphite gaskets find wide application in various industrial sectors.
Properties of Graphite Gaskets
Graphite gaskets are made from expanded graphite, a material with exceptional physical and chemical properties:
- Thermal Resistance – Graphite gaskets can withstand temperatures up to 3000 °C in an inert environment and approximately 550 °C in oxidative environments.
- Chemical Stability – Resistant to a wide range of aggressive chemicals, acids, bases, and organic solvents.
- Excellent Sealing Ability – Due to its flexibility and ability to adapt to irregular surfaces, it can create seals even in demanding conditions with variable pressures.
- Low Permeability – Graphite is almost impermeable to gases and liquids, ensuring effective sealing even in environments with extreme pressures.
Main Areas of Use for Graphite Gaskets
- Energy Sector – Graphite gaskets are widely used in power plants, especially in high-pressure steam boilers, where their high resistance to temperatures and pressures is utilized. They are used to seal flange joints, valves, and other critical parts of steam and hot water transport systems.
- Petrochemical Industry – In refineries and chemical plants, graphite gaskets are used in environments with aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. Typical applications include sealing vessels, pipelines, and valves exposed to acids, bases, or other corrosive substances.
- Chemical Industry – Graphite gaskets find application in chemical production, where it is necessary to seal systems transporting aggressive media at high temperatures. Graphite materials are indispensable here due to their resistance to chemical reactions, whether in the production of acids, fertilizers, or solvents.
- Automotive Industry – In the automotive industry, graphite gaskets are mainly used in engine systems, where they are found in environments with high temperatures and pressures. Typical examples are exhaust system gaskets or cylinder head gaskets, where it is necessary to withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, and pressures.
- Steel and Metallurgical Industry – In the steel and metallurgical industry, graphite gaskets are used in high-temperature applications, such as metal melting furnaces or gas and vapor exhaust systems. Due to their resistance to high temperatures and chemical influences, they are ideal for environments where conventional sealing materials fail.
- Pharmaceutical Industry – Even in demanding hygienic conditions of pharmaceutical production, graphite gaskets can be used, especially where high temperatures or aggressive chemicals are involved. In pharmaceutical production, not only sealing ability is important, but also the chemical inertness of the material to prevent product contamination.
Further details about the material can be found at this link.
Technical Properties of the Material
The table contains detailed properties of expanded graphite used for gasket manufacturing. These properties were tested on material with a thickness of 1.5 mm.
| Property | Standard | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | DIN 28090-2 | g/cm3 | 1,5 |
| Density (pure graphite) | DIN 28090-2 | g/cm3 | 1,0 |
| Total Sulfur Content | ASTM D5016 | ppm | / |
| Chloride Content | FSA NMG 202 | ppm | 20 |
| Fluoride Content | FSA NMG 203 | ppm | 20 |
| Ash Content | DIN 51903 | % | 1 |
| Compressibility | ASTM F36A | % | 35 |
| Recovery | ASTM F36A | % | 17 |
| Residual Stress (50 MPa, 300°C, 16 h) | DIN 52913 | MPa | 49 |
| Specific Leak Rate | DIN 3535-6 | mg/(s·m) | 0,05 |
| Compression Modulus | DIN 28090-2 | ||
| – At room temperature: εKSW | % | 34 | |
| – At elevated temperature: εKSW/300°C | % | 1,2 | |
| Creep Relaxation | DIN 28090-2 | ||
| – At room temperature: εKSW | 4,2 | ||
| – At elevated temperature: εKSW/300°C | 3,3 | ||
| Operating Conditions | |||
| – Minimum Long-term Temperature | °C/°F | -200/-328 | |
| – Maximum Long-term Temperature | °C/°F | 550/1022 | |
| – Maximum Operating Pressure | bar | 200 |

